 Min Kyoon Shin, Bommy Lee, Shi Hyeong Kim, Jae Ah Lee, Geoffrey M. Spinks, Sanjeev Gambhir, Gordon G. Wallace, Mikhail E. Kozlov, Ray H. Baughman & Seon Jeong Kim
Min Kyoon Shin, Bommy Lee, Shi Hyeong Kim, Jae Ah Lee, Geoffrey M. Spinks, Sanjeev Gambhir, Gordon G. Wallace, Mikhail E. Kozlov, Ray H. Baughman & Seon Jeong Kim
Center for Bio-Artificial Muscle and Department of Biomedical Engineering, Hanyang University, Seoul 133-791, Korea.
ARC Centre of Excellence for Electromaterials Science, Intelligent Polymer Research Institute, University of Wollongong, Wollongong, New South Wales 2522, Australia.
The Alan G. MacDiarmid NanoTech Institute, University of Texas at Dallas, Richardson, Texas 75083, USA.
*Corresponding author.E-mail: sjk@hanyang.ac.kr.
원문 링크 : http://www.nature.com/ncomms/journal/v3/n1/abs/ncomms1661.html#affil-auth
Abstract
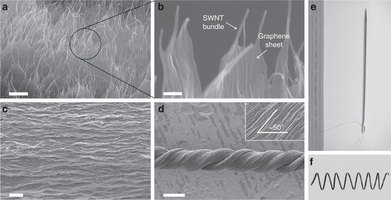
The extraordinary properties of graphene and carbon nanotubes motivate the development of methods for their use in producing continuous, strong, tough fibres. Previous work has shown that the toughness of the carbon nanotube-reinforced polymer fibres exceeds that of previously known materials. Here we show that further increased toughness results from combining carbon nanotubes and reduced graphene oxide flakes in solution-spun polymer fibres. The gravimetric toughness approaches 1,000 J g−1, far exceeding spider dragline silk (165 J g−1) and Kevlar (78 J g−1). This toughness enhancement is consistent with the observed formation of an interconnected network of partially aligned reduced graphene oxide flakes and carbon nanotubes during solution spinning, which act to deflect cracks and allow energy-consuming polymer deformation. Toughness is sensitive to the volume ratio of the reduced graphene oxide flakes to the carbon nanotubes in the spinning solution and the degree of graphene oxidation. The hybrid fibres were sewable and weavable, and could be shaped into high-modulus helical springs.